Andrea Palladio, also known as the Father of Palladianism and the Neo-Classical movements, is one of the most important architects in history.

Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/dc28ab28-eadf-4fc6-b11b-33fe1894859c by Andrea Palladio
About His Life
Andrea di Pietro dalla Gondola, was born in Padua on November 30, 1508. In 1521, he became an apprentice of a local stone cutter. Then, at the age of 16, he joined the stone cutters’ guild. In 1938, the famous writer Gian Giorgio Trissino noticed his skill and thus became an admirer. Additionally, Trissino gave Andrea his humanist name Palladio, inspired by the wisdom of the Greek goddess Pallas Athene.

Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/ee4d5e06-db59-40a5-b61d-805a691e4b35 by Luigi Baldin
Andrea Palladio continued his study of ancient Roman architecture and perfected classic style, creating elegant architecture while keeping Veneto’s rich traditions. Based on his research, Palladio wrote a series of books called Antiquity of Rome (1554-1570). The complete series first printed in 1570 under the title “I quattro libri dell’architettura” (Four Books of Architecture) in Venice. Additionally, his works on architectural theory and his famous buildings expressing Renaissance principles.
His Major Works
- Villa Godi Malinverni(c. 1538-1542): Located in Lonedo, it was his first independent project. Moreover, his simplistic, austere style shows some influence from ancient architecture, but the emphasis on crisp cubic shapes heralds his mature style.

Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/b02698bc-b9f8-47fc-ae78-91ee8bd63c6d by hans a rosbach
- Casa Civena (1540-1546): Located in Vicenza, the structure resembles the style of the High Roman Renaissance, due to its double Corinthian pilasters above the first floor. Some believe the architect gained inspiration for this piece from the publications of Sebastiano Serlio.
- Villa Capra or Rotonda (1550-1551, with later changes): The most famous of his Veneto works, is located near Vicenza. It is a simplified cuboid shape, topped with a dome over a central circular hall. In addition, it has four identical temple front porches, one on each side of the building.

Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/27c02961-128e-414c-afc2-cc6359cde653
- Villa Valmarana 1542 (built 1542 – 1560): Built for Giuseppe and Antonio Valmarana, Vigardolo di Monticello Conte Otto in the Province of Vicenza.
- Villa Barbaro (1554 – 1558): Also known as Villa di Maser, Palladio built it for Daniele and Marcantonio Barbaro in Maser, Province of Treviso, Italy.
- Villa Emo (built 1559 – 1565): Built for Leonardo Emo, Fanzolo di Vedelago, Province of Treviso, in Veneto, Italy.

image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/777431eb-1335-4228-b288-8f4d3965a737 by Hans A. Rosbach
- The Monastery of San Giorgio Maggiore: Palladio’s first work in Venice, this was the refectory of the construction of which he completed in 1560-1562. Moreover, it has a basilica plan with apsidal transept arms and a deep choir.

image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/e845453b-e191-4419-a2f7-a714f813011c by Indyblue
Palladio’s Legacy
In the entire development of Western architecture, Palladio is still one the most influential figures. Additionally, many others imitated his palaces and villas for 400 years. The use of Classical elements of ancient Roman and Greek architecture, through balanced, rational, and geometric forms were the basis of Palladian architecture. Moreover, these elements define the classical aspects of the style.
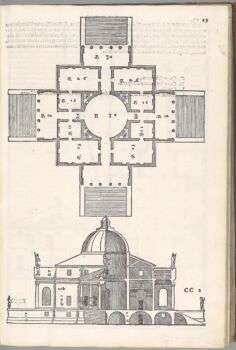
Andrea Palladio was the first architect to systematize the plan of a house and to consistently use the facade of the ancient Greco-Roman temple as a portico, or covered portico supported by columns. Additionally, his work “I quattro libri dell’architettura,” produced a treatise on architecture which, by popularizing classical decorative details, is likely the most influential architectural model book ever printed.
The influence of Palladio’s publications and his architectural style reached its peak in 18th-century architecture. When the style known as Palladianism was created and spread over the world.
Info sources:
http://www.britannica.com/biography/Andrea-Palladio
http://study.com/academy/lesson/palladian-architecture-classical-and-non-classical-features.html
http://biography.yourdictionary.com/andrea-palladio
Please also visit https://www.idesign.wiki/
