Photovoltaic Solar Panels absorb
Photovoltaic Solar Panels absorb sunlight as a source of energy to generate electricity. Solar is the greenest, most secure, renewable, sustainable and easy-to-produce energy at our disposal on earth today. Yet the world economic system is still stuck on unsustainable fossil fuels.

image source:https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/aa091193-a5b6-4e6d-8df2-64ba7c734c08 by Living Off Grid

Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/4f38c25d-b6a2-4c02-9d11-43fce194227f by Peter Blanchard
A 2017 report from the International Energy Agency shows that solar has become the world’s fastest-growing power source, marking the first time solar energy’s growth has surpassed all the other fuels. In the coming years, we will be enjoying the benefits of solar-generated electricity in one way or another.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
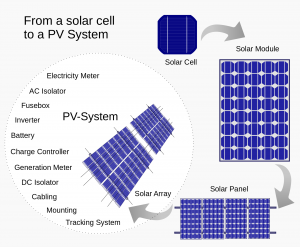
When photons hit a solar cell, they let electrons loose from their atoms. If conductors are attached to the positive and negative cell sides, it forms an electrical circuit. When electrons flow through a circuit, they generate electricity. Multiple cells make up a solar panel, and multiple panels (modules) can be wired together to form a solar array. The more panels you can deploy, the more energy you can expect to generate.
image source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_cell_panel#/media/File:From_a_solar_cell_to_a_PV_system.svg
What are Solar Panels Made of?
Photovoltaic (PV) solar panels are built of many solar cells. Solar cells are composed of silicon, like semiconductors. They are built with a positive layer and a negative layer that create an electric field, just like in a battery. A typical solar module includes a glass casing that offers durability and protection. Under the glass exterior, the panel also has a layer for insulation which avoids heat dissipation.
How Do Solar Panels Generate Electricity?
PV solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity. With DC PV solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity. With DC electricity, electrons flow in one direction around a circuit. This example shows a battery powering a light bulb. Through the lamp, electrons move from the negative side of the battery to the positive side.
With AC (alternating current) electricity, electrons are periodically pushed and pulled, much like the cylinder in a car engine. Generators create AC electricity when a coil of wire is spun next to a magnet. Many different energy sources can “turn the handle” of this generator, such as gas or diesel fuel, hydroelectricity, nuclear, coal, wind, or solar.
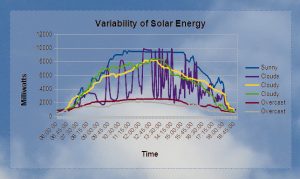
image source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_cell_panel#/media/File:Variability_of_Solar_Energy.jpg
Info source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_panel
