Synthetic fibres or man-made textile fibres are produced completely from chemical substances. These fibres are created with particular properties. They are non-biodegradable and can remain in the environment for many years.

Image source: https://startupfashion.com/fashion-archives-history-synthetic-fiber/
What are synthetic fibres?
Synthetic fibres are man-made fibres made mainly from non-renewable coal and oil refined into monomers, which join together in a process called polymerisation. Their chemical composition, structure, and properties are significantly modified during the manufacturing process. They do not deteriorate easily. Synthetic fibres can be mass-produced to about any set of wanted characteristics. Millions of tons are produced every year.
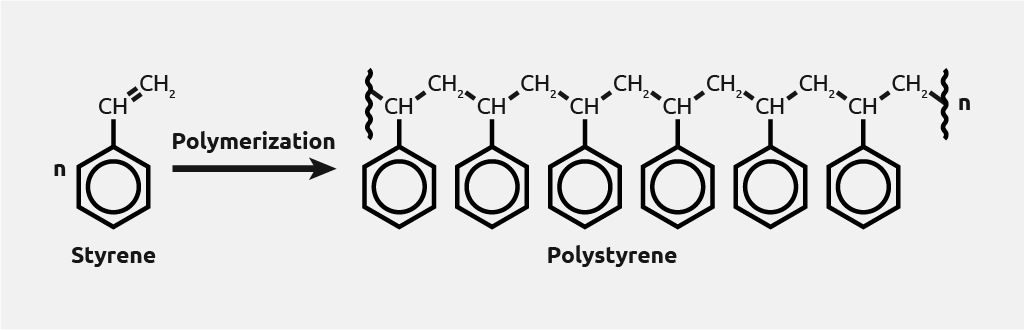
Image source: https://www.syrris.com/applications/polymerization/
Origins and first developments

Image source: https://www.britannica.com/biography/Joseph-Wilson-Swan
The first semisynthetic fibre was glass. One of the first artificial fibres was invented by Joseph Swan in the early 1880s. His fibre derived from a cellulose liquid, produced by chemically modifying the fibre contained in tree bark. Swan understood the potential of the fibre to revolutionize textile manufacturing, so in 1885, he revealed his synthetic material fabrics at the International Inventions Exhibition in London. Hilaire de Chardonnet was a French engineer and industrialist. He invented the first artificial silk, which he called “Chardonnet silk”. He displayed his product at the Paris Exhibition of 1889. In 1894, the English chemist Charles Frederick Cross and his collaborators created the fibre “viscose“. The name derives from the reaction product of carbon disulfide and cellulose in basic conditions that gave a highly viscous xanthate solution. The first commercial viscose was rayon produced by the UK company Courtaulds in 1905. A similar product was invented in 1865, known as cellulose acetate. Rayon and acetate are artificial fibres, but not completely synthetic because they are made from wood.
Nylon, the first fully synthetic fibre, was developed by Wallace Carothers, an American researcher at the chemical firm DuPont in the 1930s. It soon made its introduction in the United States as a replacement for silk, just in time for the rationing during World War II. It was used in the manufacturing of stockings and for military equipment. The first polyester fibre was patented in Britain in 1928 by the International General Electric company.
Characteristics
All synthetic fibres have rod-like structures, long, circular when cut in a cross-section. The synthetic fabrics have a sleek and shiny exterior. They are lightweight but very strong, more than natural fabrics. They are all poor conductors of heat and usually easily maintainable, with less creasing. They dry quickly and have natural elasticity and flexibility. These fabrics are very inexpensive. Synthetic fabrics do not have the breathability of natural fabrics. They do not absorb moisture, which makes them rather uncomfortable on the skin. All of them melt with a chemical odour when put to flame and leave molten bead as residue. The cost to the environment due to the manufacture, use and disposal of synthetic fabrics are many, for example, air pollution and water pollution.

Image source:https://pxhere.com/en/photo/1117271
Types of man-made fibres

Image source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spandex
- Acrylic: good strength with good elastic properties; it doesn’t crease, has poor absorbency but is a decent insulator if the crimp is added to imitate wool fibres. it’s used for jumpers and other knitted clothing that appears like wool, fake fur jackets.
- Polyester: Hardwearing with good enduringness, good elasticity but poor absorbency, a highly versatile fibre. Clothing and sportswear.
- Nylon (polyamide): A hardwearing fibre with good strength, has good elasticity so doesn’t crease and is resists chemicals, not absorbent and melts easy. it’s used for parachutes, tents, rucksacks, sportswear, rope and carpets.
- Elastane: Highly elastic and stretchy, strong and hardwearing. it’s employed in clothing like leotards, swimming costumes and gym clothing, mixed with cotton in T-shirts for a better fit.
Info sources:
https://sewguide.com/synthetic-fabrics-fibers/
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/z74bcj6/revision/5
https://www.britannica.com/technology/synthetic-fiber
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/z74bcj6/revision/5
