Palladianism is named after the Renaissance architect Andrea Palladio, whose work had a relevant influence on architecture in Europe from the 18th century to the present day.

Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/dc28ab28-eadf-4fc6-b11b-33fe1894859c by Andrea Palladio
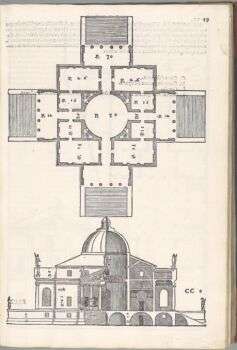
Origins and Features of this Style
Palladio redesigned Roman architecture for contemporary use and published “I Quattro Libri dell’Architettura,” which was translated and published across Europe. His architecture emphasized symmetry, proportion, and his codification of Classical Orders. He used classical forms and decorative motifs. These are the main features:
- Corinthian columns and acanthus leaves
- Shells, a symbol of the Roman goddess Venus
- Pediments and masks used as decorations inside and outside of buildings
- Terms are used to recall the Roman god, Terminus, as boundary markers

Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/b1dbae9b-d78f-4a12-90af-1a91991cc4c2 by orangeaurochs
Architects
Andrea Palladio’s style strongly recalls Classical times, and his concepts are based on ancient Roman architecture. He wrote “I Quattro Libri dell’Architettura” which contains illustrations and explanations of his architecture. His first commission was Villa Godi. It features many elements of the architecture of castles, such as “La colombaia.”

Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/b02698bc-b9f8-47fc-ae78-91ee8bd63c6d by hans a rosbach
English Palladianism
Chiswick House, finished between 1725 and 1729, was designed by Lord Burlington. The centralized structure and square plan of the estate was inspired by Andrea Palladio’s Villa Rotonda near Vicenza (Italy).

Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/1c71e58d-4c37-47c1-9360-c16d6ddd6cbf by Maxwell Hamilton

Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/6b91eaff-fba8-42c1-a1a9-ad76f5677e2c by It’s No Game
Wanstead House was designed by Colen Campbell: an architect and pioneer of the Palladian style. The grand entrance portico, arched windows, huge blocks of basement, and pavilions adorned by arched “Venetian” windows at Wanstead will later become key Palladian architecture features.
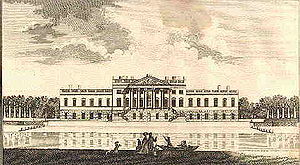
Image source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wanstead_House
Palladian Furniture
Architects were interested in buildings, grounds, and gardens, but furniture was different because it had to be in line with other elements. William Kent, a furniture designer linked to Palladian architecture, designed pieces for Burlington’s villa and Chiswick House. The “Kentian” style was ornate, unique and fashioned with gold details.

Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/c328d800-c267-458e-a8b2-5589a8a0ae65 by Images George Rex
Benjamin Goodison is another important designer, who part of the Royal cabinet under George II of Great Britain. For his work, he took inspiration from the Neo-Palladian designs of William Kent.


Info source: https://www.vam.ac.uk/collections/palladianism
