The First Industrial Revolution marked a period of development that transformed rural, agrarian societies into industrialized urban ones, switching from hand production methods to factory systems.

image source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Industrial_Revolution#/media/File:Crystal_Palace_interior.jpg
Modern historians set this period apart from the Second Industrial Revolution that took place between 1840 and 1870, characterized by rapid advances in the steel, electric, and automobile industries, led by the United States of America and Germany.
The First Industrial Revolution began in Britain around 1760 and spread to the rest of the world by the 1830s. It was a period of massive economic, technological, social, and cultural change, which marks a major turning point in history since almost every aspect of our daily life was influenced in some way.
What was revolutionized?
INDUSTRY AND ECONOMY
- The invention of steam power to power the new factory system;
- The textile industry was transformed by the invention of new machines and machine tools, allowing for much higher production at a lower cost;
- Industrial technologies affected farming and contributed to the start of the agricultural revolution;
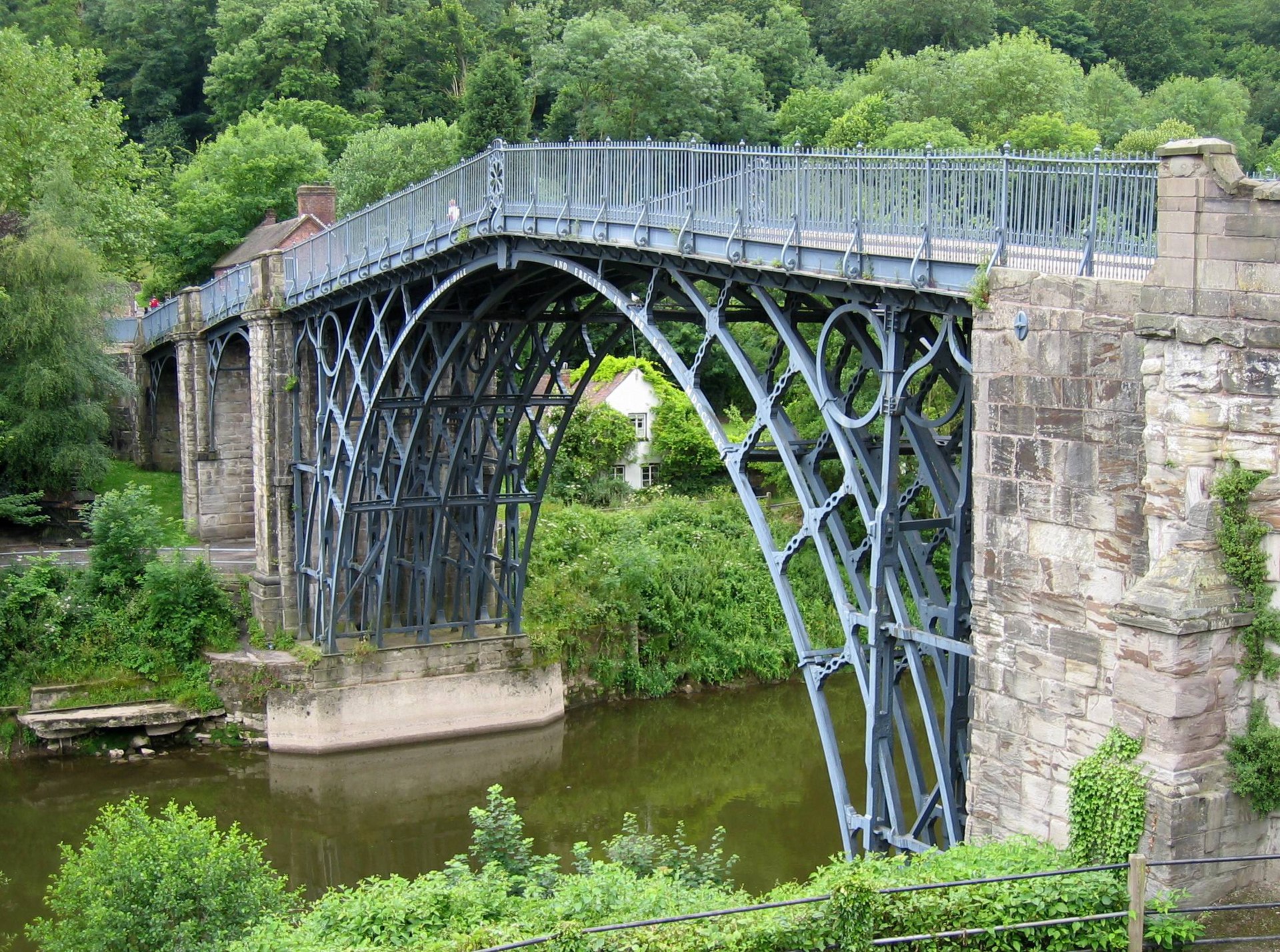

image source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Industrial_Revolution#/media/File:Ironbridge_6.jpg
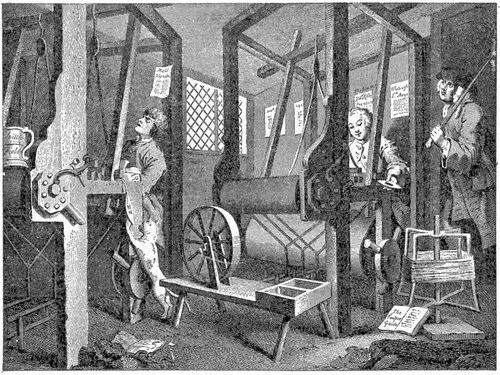
image source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Industrial_Revolution#/media/File:Hand-loom_weaving.jpg
- The improvement of iron-making techniques, metallurgy, and chemical production. The Coalbrookdale Bridge on the Severn River is an exemplary result of these innovations: engineered by J.Wilkinson and T.Pritchard, it was the first civil engineering structure in the world to be made entirely of cast iron;
- The use of coal soared over the traditional charcoal since melting iron ore with coke, a material made by heating coal, was cheaper and produced higher-quality metal, which led coal to eventually replace wood;
- The first canals and then railways allowed workers and materials to be moved cheaper and more efficiently;
- The banking industry developed to meet the needs of entrepreneurs, providing finance opportunities that allowed the industries to expand.
Society and culture
- The rapid urbanization led to an unprecedented rise in the rate of population growth, bringing significant challenges such as overcrowded cities suffering from pollution, inadequate sanitation, and a lack of clean drinking water;

image source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Industrial_Revolution#/media/File:Powerloom_weaving_in_1835.jpg
- Industrialization improved living standards for the middle and upper classes, while poor and working-class people continued to struggle. Working in factories was increasingly tedious and dangerous since workers were forced to work long hours for pitifully low wages. Such dramatic changes fueled debates regarding child labor, public health, and working conditions, as well as opposition groups such as the “Luddites”, known for their violent resistance.
info source:
