Artificial intelligence (AI) is a wide-ranging category of computer science involved with developing smart machines able of performing tasks that typically demand human intelligence. AI has various applications like medical diagnoses, computer search engines, and voice or handwriting recognition.

mage source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/4984f318-2feb-4256-ad42-a70de04807b4
What is AI?
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to machines programmed to simulate human intelligence and actions. The term can be applied to systems supplied with human intellectual processes, such as the ability to reason, discover meaning, generalize, or learn from experience. Since the 1940s and the development of the digital computer, technological developments showed computers can be programmed to execute very complex tasks with high proficiency. The prototypical aspect of artificial intelligence is its capability to rationalize and take actions that have the best chance of achieving a specific result.

Image source:https://www.pxfuel.com/en/free-photo-qaulj
History
The history of Artificial Intelligence starts with the advent of electronic computing. Here are some of the most relevant events in the evolution of AI:

by Joanna Goodrich
Image source: https://spectrum.ieee.org/the-institute/ieee-history/how-ibms-deep-blue-beat-world-champion-chess-player-garry-kasparov
- 1950: Alan Turing publishes Computing Machinery and Intelligence. The scientist, famous for decoding the Nazi’s ENIGMA code during WWII, proposed to answer the question “can a machine think?” and introduces the Turing Test which can tell if a computer can demonstrate the same intelligence as a human or achieve the same results. The debate over the value of the Turing test continues nowadays.
- 1956: John McCarthy (creator of the Lisp language) invents the term “artificial intelligence” at the first-ever AI conference at Dartmouth College. Later that year, Allen Newell, J.C. Shaw, and Herbert Simon built the Logic Theorist, the first running AI software program.
- 1967: Frank Rosenblatt develops the Mark 1 Perceptron, the first computer-based on a neural network that acquired new knowledge by trial and error.
- 1980: Neural networks featuring backpropagation, algorithms for training the network, become widely used in AI applications.
- 1997: IBM‘s Deep Blue defeats the world chess champion, Garry Kasparov, in a chess match.
- 2011: IBM Watson knocks down champions Ken Jennings and Brad Rutter at Jeopardy!
- 2015: Baidu supercomputer employs a special deep neural network type called “convolutional neural network” to identify and classify images with a higher rate of accuracy than the average human.
- 2016: DeepMind’s AlphaGo program, powered by a deep neural network, defeats Lee Sodol, world champion Go player, in a five-game match. Google purchased DeepMind for $400 million.
Types of AI
Artificial intelligence can be divided into two different classes:
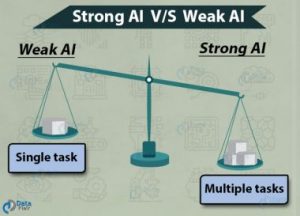
Image source: https://data-flair.training/blogs/artificial-intelligence-ai-tutorial/
- Weak artificial intelligence integrates a system designed to execute one specific assignment. Weak AI systems include video games and personal assistants.
- Strong artificial intelligence systems perform tasks considered to be human-like. These are often more complex and complicated systems. They are programmed to manage situations where they may be needed to problem-solve without having a person intervening. These systems are often used in applications like self-driving cars or hospital operating rooms.
Learning techniques
Two types of learning techniques can be applied in AI development:
- Machine learning learns by itself. It reprograms itself, as it absorbs more data, to perform the specific task it’s designed to complete with increasingly higher precision.
- Deep learning is a subset of machine-learning application that can perform a specific task with increasingly more elevated accuracy, without human intervention.

Image source: https://semiengineering.com/deep-learning-spreads/
Examples of AI

Image source: https://www.commonsense.org/education/articles/compare-the-privacy-practices-of-the-most-popular-smart-speakers-with-virtual-assistants
- Smart assistants
- Disease mapping and prediction tools
- Manufacturing and drone robots
- Optimized, personalized healthcare treatment recommendations
- Marketing and customer service conversational bots
- Robo-advisors for stock trading
- Spam filters on email
- Social media monitoring tools
- Recommendation algorithm from Spotify and Netflix
Info source:
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/a/artificial-intelligence-ai.asp
https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/what-is-artificial-intelligence
https://www.britannica.com/technology/artificial-intelligence
https://builtin.com/artificial-intelligence
https://www.tenacityworks.com/tw-workshop/artificial-intelligence-why-you-should-embrace-it/
